The Key to Inner Youth, or Why It’s Worth Taking Supplementation Seriously
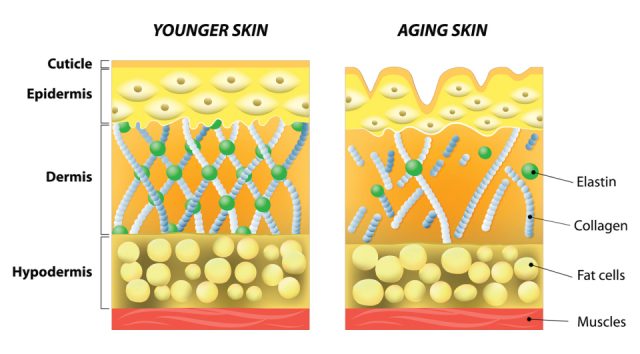
Collagen is one of the most important structural proteins in our body, literally holding our tissues together. The health of our skin, joints, muscles, bones, hair, and nails largely depends on the adequate presence of collagen. However, few people realize that after the age of 25, the body’s natural collagen production begins to decline, and by the time we reach our 40s, this decline becomes dramatic. This is why the skin sags, joints become stiffer, hair thins, and nails become brittle.
What Exactly Is Collagen and Why Is It Important?
Collagen is a fibrous protein that makes up about 30% of the body’s protein content and 70-80% of the skin’s protein content. Its role is to provide elasticity, structure, and strength to tissues. In the skin, it ensures hydration; in the joints, it acts as a cushion; and in the bones, it provides structural stability. Therefore, maintaining a proper level of collagen is not only a beauty concern but also a matter of functional health.
The Role of Collagen in Health – It’s About More Than Just Beautiful Skin
Collagen is one of the most crucial structural proteins in the human body, accounting for approximately 30% of our total protein content. It is found in large quantities in the skin, bones, tendons, cartilage, and connective tissues [1]. As we age, collagen production naturally decreases, leading to dry skin, wrinkles, and joint pain [2].
Why Is External Collagen Supplementation Necessary?
After the age of 25, the body produces about 1–1.5% less collagen each year. By the age of 40, this can result in a loss of up to 25% [3]. Collagen obtained from natural sources, such as bone broth, skin-on meats, or gelatin, is less effective because it may not reach the tissues where it’s needed. Let’s face it, few people today have the time to cook therapeutic bone broth (slow-cooked for at least 8 hours, sometimes even 24–48 hours), consume it regularly, or incorporate it into their daily routine. Moreover, stomach acid and the digestive system break down the amino acids in collagen, so there’s no guarantee they will reach the right places. Therefore, targeted supplementation with hydrolyzed (more easily absorbed) collagen peptides is a much more effective solution.
Hydrolyzed collagen peptides are proven to be well-absorbed and enhance the body’s own collagen synthesis [4].
Types of Collagen – Not All Are Created Equal
There are at least 28 different types of collagen known, but the most important ones for the body are:
- Type I: The most common type, primarily found in the skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments. It is crucial in the fight against skin aging due to its tightening and skin-structure-improving effects.
- Type II: Found mainly in cartilage and key for joint health.
- Type III: Present in elastic tissues, such as arterial walls and internal organs. It often occurs alongside Type I.
- Types V, IX, X: These play roles in specialized tissues, such as the placenta, hair, and bone regeneration.
Clinical studies confirm that peptides of Type I and III collagen improve skin elasticity, hydration, and reduce wrinkles, while Type II collagen improves joint pain and mobility [6][7].
Sources of Different Types of Collagen
- Type I: Skin, bones, tendons – most common, animal-derived (beef, pork).
- Type II: Cartilage – mainly sourced from chicken.
- Type III: Elastic tissues (e.g., arteries) – often combined with Type I.
- Marine collagen: Derived from fish, offering Types I and III with superior bioavailability (over 90%) in the form of low molecular weight peptides.
What Forms Does Collagen Come In?
- Hydrolyzed powder: Best absorption, tasteless, easily mixable with food or drinks.
- Capsules: Convenient, precise dosage, but lower doses (2–3 grams per capsule).
- Drink powders: Combined with vitamins and antioxidants.
- Liquid: Rapid absorption, but beware—often high in sugar.
Why Is Marine Collagen the Most Effective?
Marine collagen (primarily derived from fish skin) has higher biological availability than bovine or porcine collagen. This is due to its lower molecular weight (approximately 2,000–3,000 Da), which allows for faster absorption [8].
The main advantages of marine collagen include:
- High levels of Type I collagen.
- High bioavailability – thanks to its smaller molecular size, it is absorbed faster and more effectively than bovine or porcine collagen.
- Gentle processing – free from hormones or antibiotics, which may be present in other animal-derived collagens.
- Amino acid profile: Rich in glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline, all of which directly participate in collagen synthesis.
According to a 2021 study, 12 weeks of marine collagen application significantly improved skin moisture and reduced wrinkles compared to the placebo group [9].
Zinzino Collagen⁺ Boost – Science-Based Innovation

While many collagen supplements are available on the market, Zinzino Collagen⁺ Boost stands out in several ways—not just in terms of the type of collagen but also in its active ingredients, absorption support, and scientific backing.
Zinzino Collagen Boost is not just another collagen drink—it is a scientifically developed formulation built on clinical research, containing synergistic (mutually enhancing) ingredients.
What Makes It Unique?
- Verisol® Marine Collagen Peptides Behind the Verisol® brand name lies clinically tested marine collagen peptides, which specifically improve skin elasticity, moisture, and reduce wrinkles [10].
- Synergy of Supporting Micronutrients
- Vitamin C: Essential for the body’s own collagen production and also acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells.
- Hyaluronic Acid: Increases skin moisture, hydrating from within.
- Pre- and Probiotics: Chicory root fiber and Lactobacillus casei fermented metabolites balance gut flora, indirectly improving nutrient absorption.
- Acerola and Blackcurrant Extract: Natural antioxidants, extra Vitamin C sources.
- Minerals – such as silicon, zinc, biotin, which play key roles in the health of skin, hair, and nails.
- Rice Bran Ceramides: Help maintain the skin’s water retention capacity.
- Pure Formula, Free of Artificial Additives Sugar-free, preservative-free, no artificial coloring. This not only makes it healthier but also enhances the absorption of active ingredients.
- Eco-friendly Source – Sourced from sustainable fishing practices.
- 10-Day Program: An intensive course to quickly restore collagen levels.
Who Should Consider Collagen Supplementation?
- Everyone over 25–30 who wants to preserve the firmness and youthfulness of their skin.
- Athletes and those leading active lifestyles, to maintain the health of joints and ligaments.
- Those suffering from joint pain, as supplementary therapy.
- Individuals with skin problems, hair loss, or weak nails.
- During lifestyle changes or pregnancy, to preserve skin elasticity and regain skin tightness.
- Women before and after menopause, as hormonal changes affect collagen production.
- Vegans who do not consume animal-based bone or skin sources – targeted supplementation is especially important in this case (though collagen itself is not vegan).
How Much Should You Take?
The daily dose of Zinzino (1 stick/day) contains 8 grams of bioactive marine collagen peptides—a quantity clinically proven to benefit skin and connective tissue structures [10]. Regular use can yield visible results within 8–12 weeks.
Conclusion – A Unique Approach to Collagen Supplementation
Collagen is not just a trendy supplement; it is a genuine, scientifically supported tool for supporting health and beauty. Zinzino Collagen⁺ Boost offers a comprehensive solution combining premium-quality marine collagen with cutting-edge, research-backed, efficacy-enhancing ingredients. This targeted, intelligent approach to nutrition allows for long-term, sustainable results—inside and out.
References:
- Ricard-Blum, S. (2011). The collagen family. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in
biology, 3(1), a004978. - Shuster, S., Black, M. M., & McVitie, E. (1975). The influence of age and sex on skin
thickness, skin collagen and density. British Journal of Dermatology, 93(6), 639–643. - Varani, J. et al. (2006). Decreased collagen production in chronologically aged skin.
The American Journal of Pathology, 168(6), 1861–1868. - Zague, V. et al. (2018). Collagen peptides modulate the metabolism of extracellular
matrix by human dermal fibroblasts. Journal of cosmetic dermatology, 17(5),
841–849. - Shoulders, M. D., & Raines, R. T. (2009). Collagen structure and stability. Annual
review of biochemistry, 78, 929–958. - Skov, L. et al. (2021). Collagen supplementation and skin health: A systematic review.
Journal of cosmetic dermatology, 20(4), 1105–1117. - Bello, A. E., & Oesser, S. (2006). Collagen hydrolysate for the treatment of
osteoarthritis and other joint disorders. Current medical research and opinion, 22(11),
2221–2232. - Zhang, Z. et al. (2020). Marine collagen peptides promote wound healing via the TGF-
β/Smad pathway. Marine Drugs, 18(8), 389. - Proksch, E. et al. (2021). Oral supplementation of specific collagen peptides has
beneficial effects on human skin physiology: A double-blind, placebo-controlled
study. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology, 34(1), 48–56. - Zdzieblik, D. et al. (2015). Collagen peptide supplementation in women: A
randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. Journal of Medical
Nutrition & Nutraceuticals, 4(1), 13–19.
Further Professional Support:
Erika Feller
Holistic Nutrition Consultant,
Laboratory Diagnostics Specialist



